The litter layer on meadows consists of a diverse mixture of organic materials such as fallen leaves, twigs, grasses, and other plant debris. It is a protective blanket, providing insulation, moisture retention, and nutrient recycling for the meadow ecosystem.
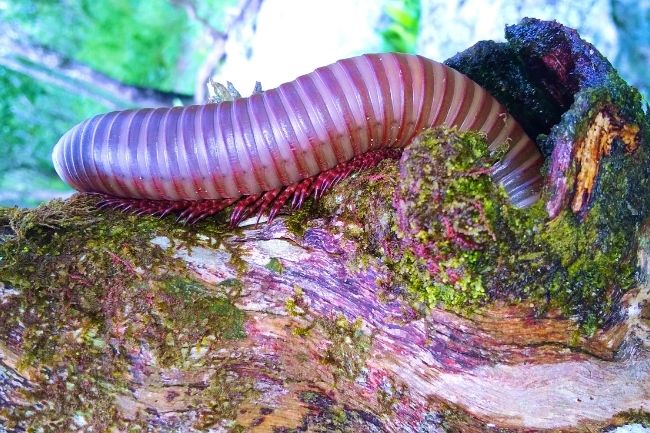
More About Millipedes
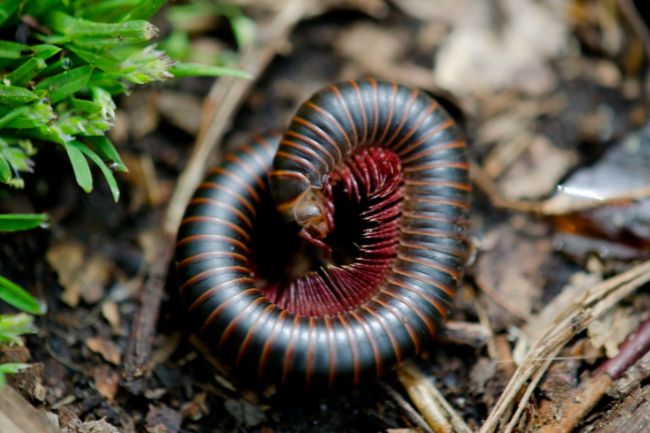
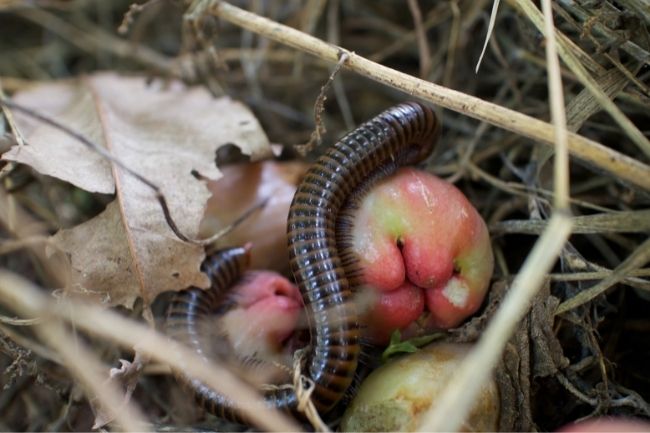
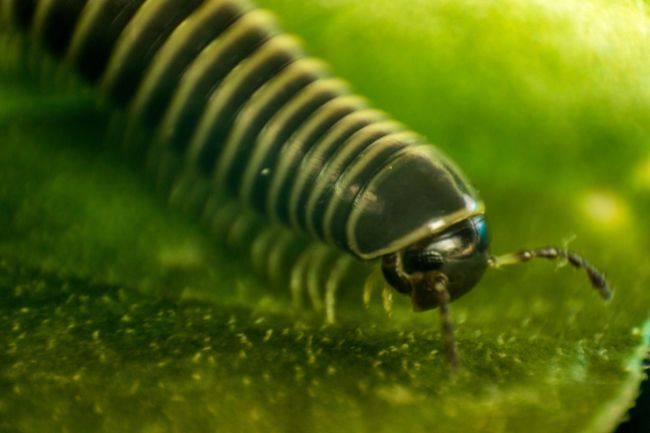
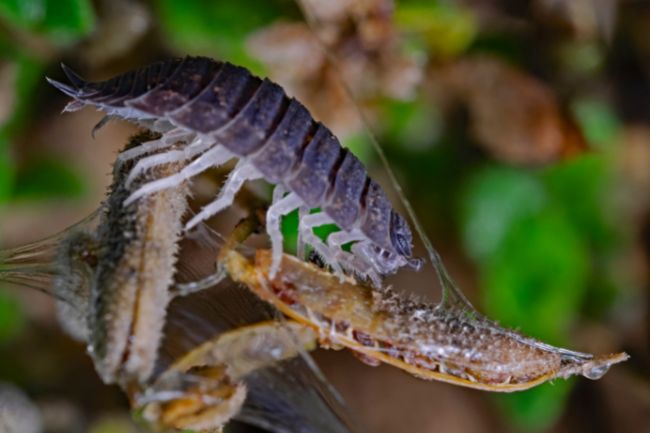
Millipedes are arthropods with elongated bodies composed of numerous segments, each bearing two pairs of legs. They play a beneficial role in ecosystems by decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients, while also serving as a food source for other animals in the food chain.
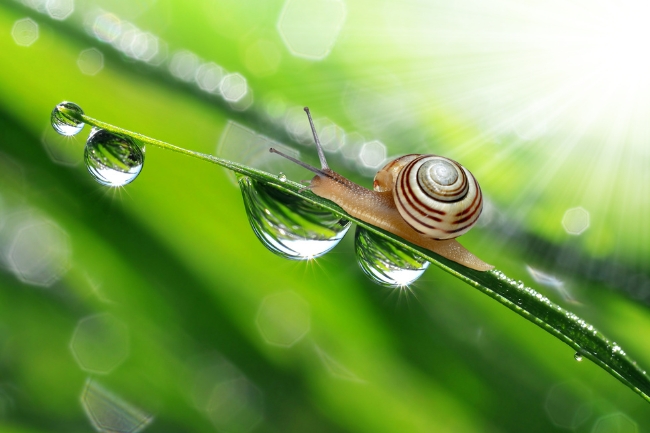
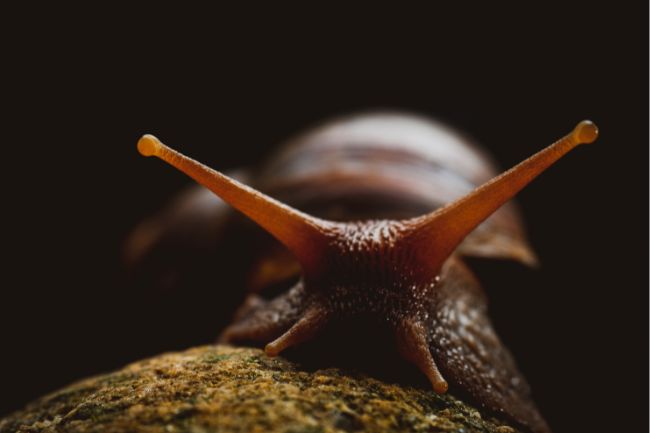
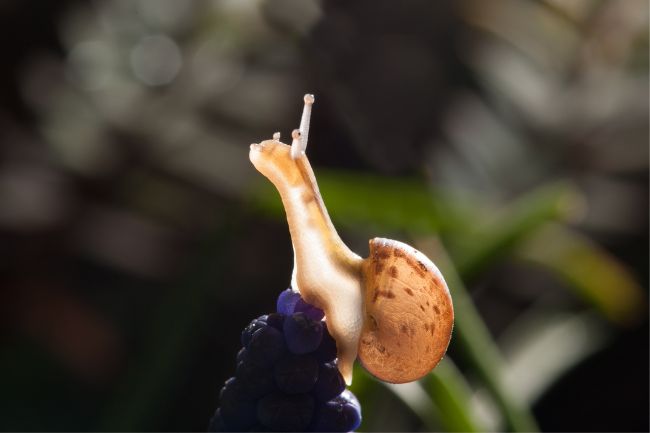
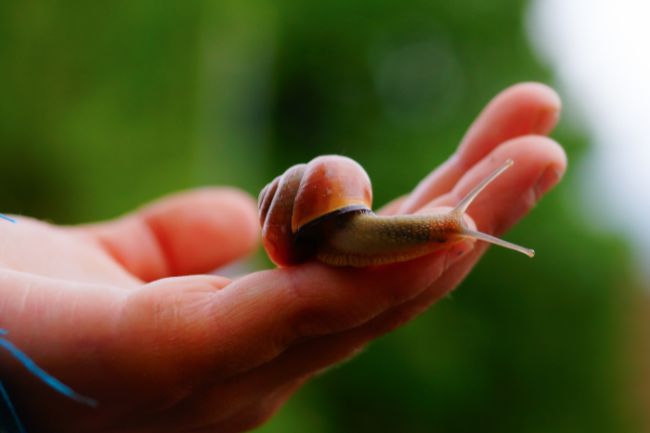
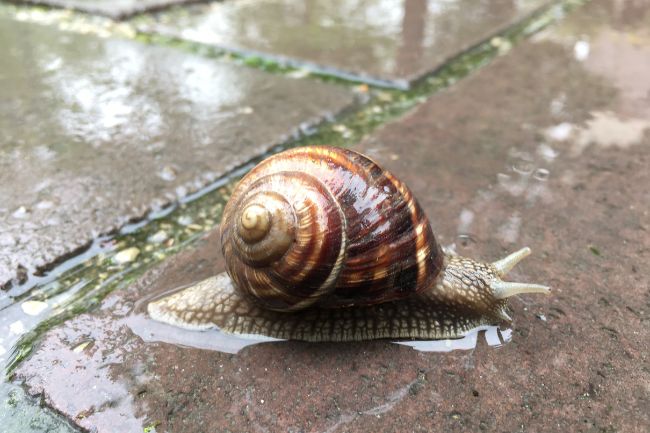
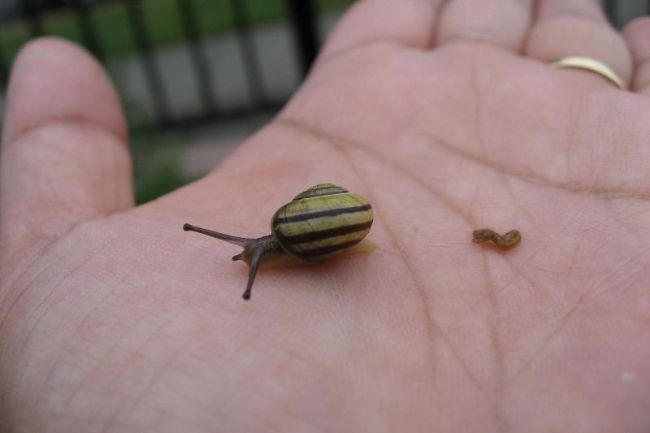
More About Snails
Snails are mollusks with a spiral-shaped shell that provides protection and serves as their home. They move slowly using a muscular foot and are known for their ability to retract into their shell when threatened, making them adaptable to a variety of habitats, from gardens to forests.
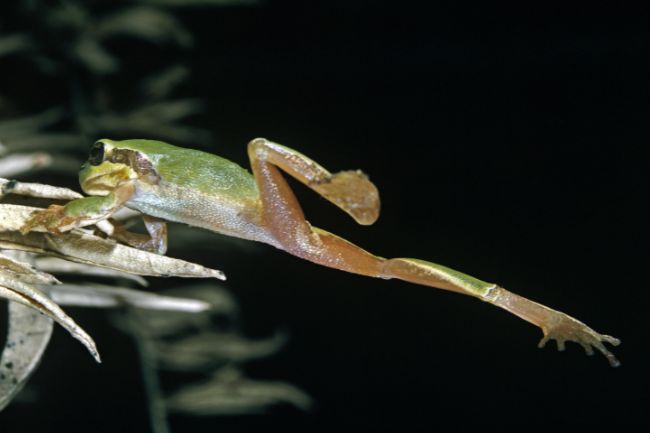
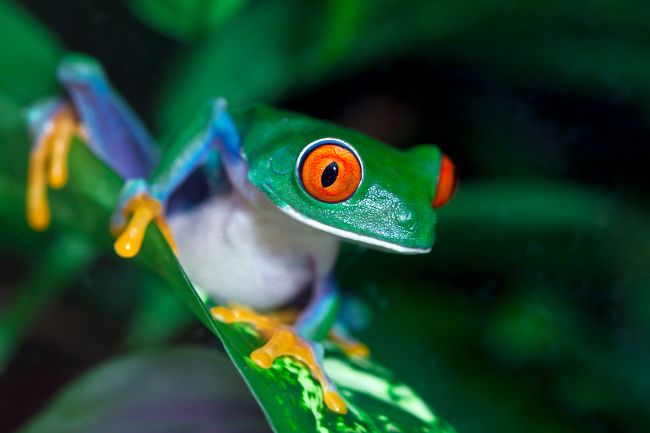
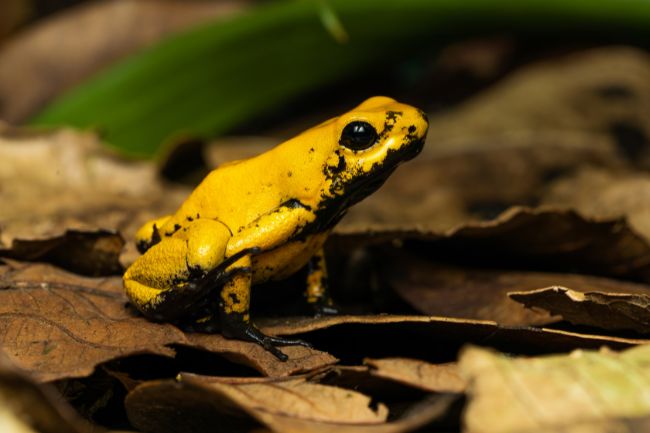
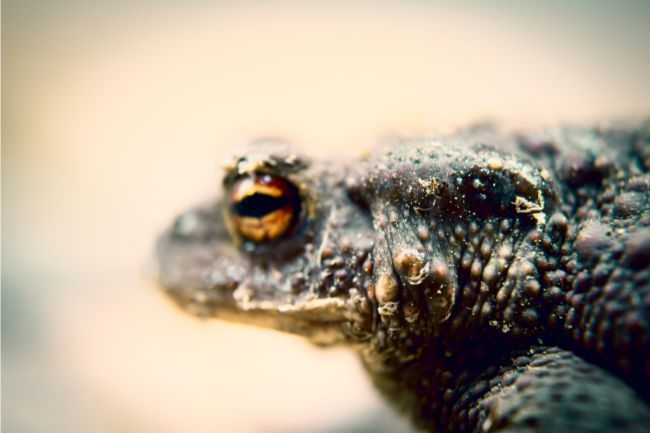
More About Frogs
Frogs are amphibians with smooth, moist skin and long hind legs adapted for jumping. They are known for their distinctive croaking sounds and their ability to live both in water and on land, playing important roles in both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems as predators and prey.
More About Woodlice
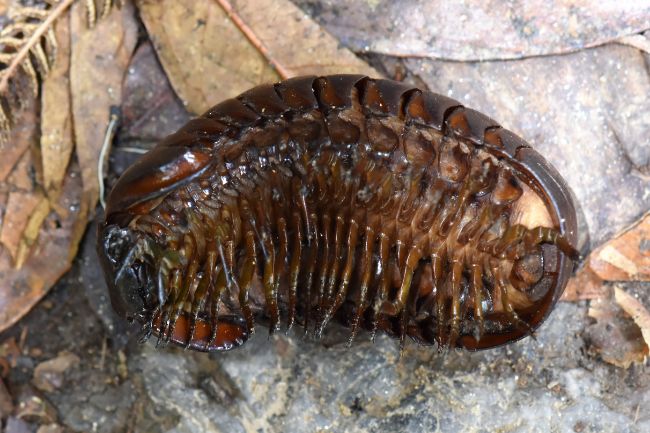
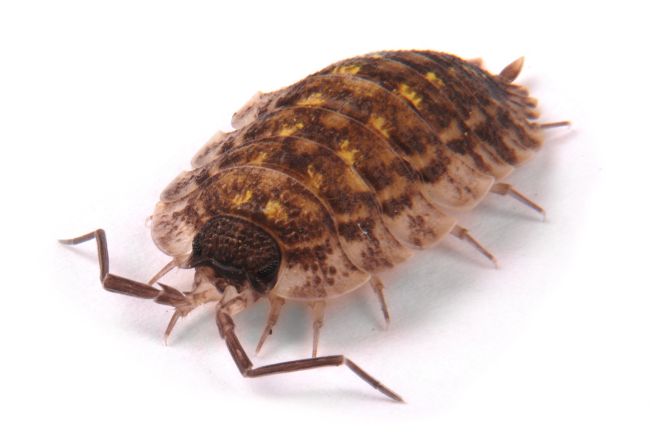
Woodlice, also known as pillbugs or sowbugs, are small crustaceans that are commonly found in damp environments, such as under logs or rocks. They feed on decaying organic matter and help in the decomposition process, playing a vital role in nutrient cycling within ecosystems.
Common Questions
What is the litter layer, and what role does it play in the ecosystem?
The litter layer is the accumulation of dead plant material, such as leaves, twigs, and decaying organic debris, on the ground in ecosystems. It plays a vital role in nutrient cycling, soil fertility, moisture retention, and providing habitat for a variety of organisms.
Which animals are commonly found in the litter layer, and how do they interact with it?
Animals commonly found in the litter layer include insects like beetles, ants, millipedes, and woodlice, as well as small mammals such as mice and shrews. They interact with the litter layer by foraging for food, nesting, and seeking shelter within the decaying organic material.
What types of food and shelter does the litter layer provide for animals?
The litter layer provides a diverse range of food and shelter for animals. Decomposing organic matter serves as a food source for detritivores and decomposers. It also offers hiding places, nesting materials, and protection from predators and extreme weather conditions.
How do decomposers contribute to the breakdown of organic matter in the litter layer?
Decomposers, such as bacteria, fungi, and certain invertebrates, play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter in the litter layer. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms, facilitating nutrient release and recycling within the ecosystem.
Are there any specific adaptations of animals for living in the litter layer?
Yes, animals in the litter layer have various adaptations for their habitat. For example, some insects have flattened bodies and camouflage to blend in with the litter, while others have mouthparts suited for feeding on decaying material. Animals may also have specialized behaviors for burrowing or navigating through the litter.
How do animals in the litter layer contribute to nutrient cycling and soil fertility?
Animals in the litter layer contribute to nutrient cycling and soil fertility through their feeding activities and waste production. As they consume organic matter, they break it down into smaller particles, promoting decomposition and nutrient release. Their waste products further enrich the soil with essential nutrients.
What are some examples of predator-prey relationships within the litter layer?
Examples of predator-prey relationships within the litter layer include interactions between ground-dwelling predators like snakes, spiders, and centipedes, and their prey, such as insects, worms, or small rodents. These relationships contribute to regulating populations and maintaining ecosystem balance.
How does the composition of the litter layer affect the diversity and abundance of animal species?
The composition of the litter layer, including its organic content and moisture levels, can influence the diversity and abundance of animal species. Different animals have specific requirements and preferences for certain types of litter, leading to variations in species composition and distribution.
Are there any risks or challenges faced by animals living in the litter layer?
Animals living in the litter layer face risks such as predation, competition for resources, and exposure to environmental fluctuations. Changes in litter composition, such as excessive moisture or nutrient imbalances, can also impact the survival and abundance of litter-dwelling organisms.
How does human activity, such as litter removal or habitat disturbance, impact the animal communities in the litter layer?
Human activity, such as excessive litter removal or habitat disturbance, can have detrimental effects on animal communities in the litter layer. Removing the litter disrupts food sources, nesting sites, and protective cover for many species. Habitat disturbance can displace or reduce populations, affecting ecosystem dynamics.